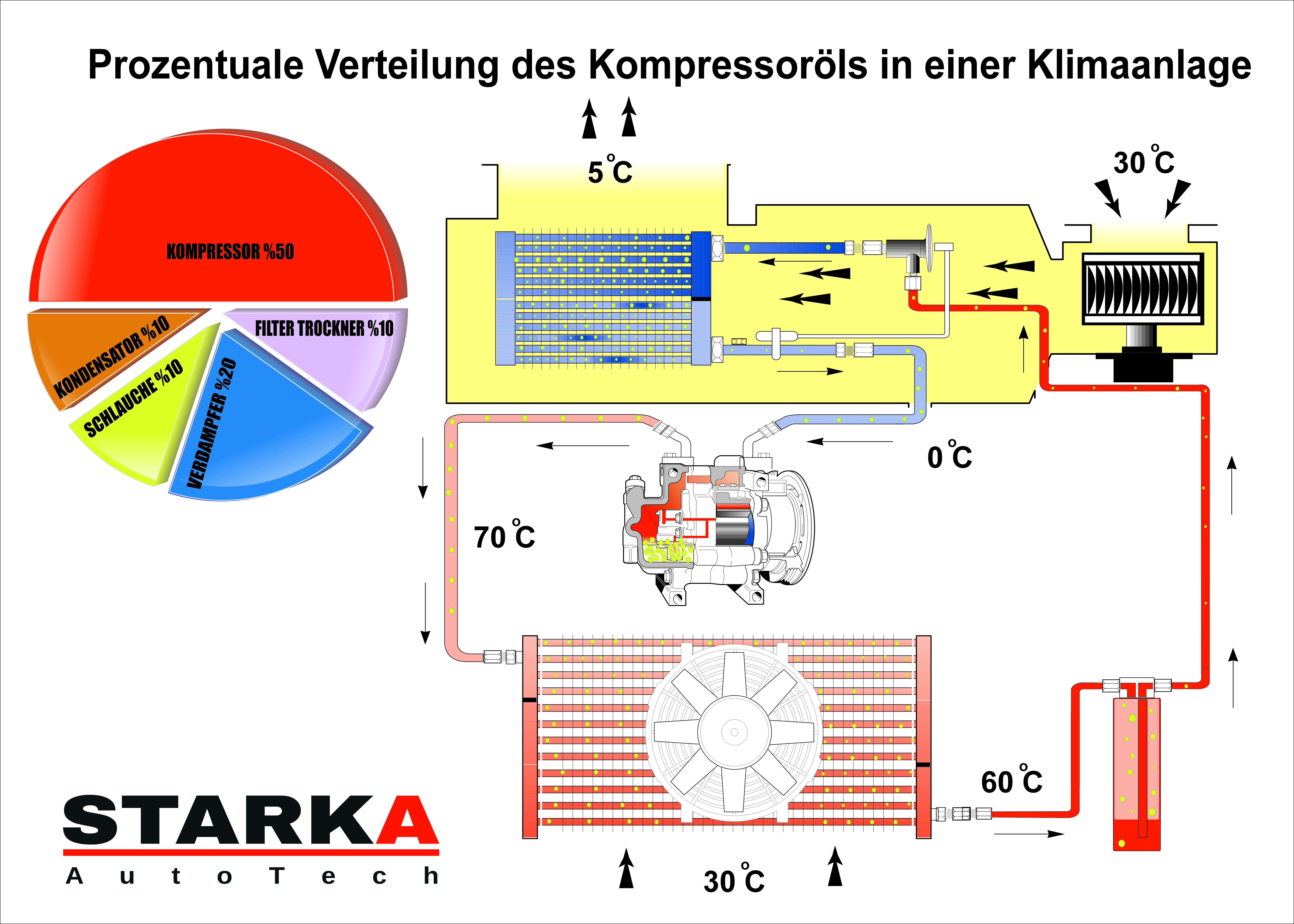
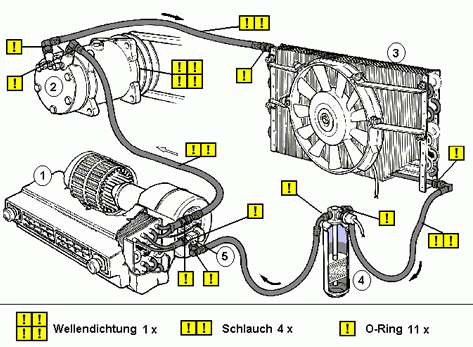
Die Abbildung zeigt die wichtigsten Quellen für Kältemittellecks nach Angaben der Automobilhersteller. Ein Kältemittelverlust von höchstens 10 bis 30 g an der Kompressorwelle wird allgemein als unvermeidlich angesehen. 42 bis 83 g Kältemittelverlust (10 bis 20 g aus dem Schlauchsystem, 2 bis 3 g aus jedem O-Ring) werden für jedes Betriebsjahr als “normal” angesehen.
In den neu entwickelten Klimaanlagen werden Trockner-Kondensator und Expansionsventil-Verdampfer zusammen hergestellt, um die Anzahl der Verbindungsstellen und damit die Leckage zu reduzieren (52 g Leckage pro Jahr).
Quelle: Emission des Kältemittels R-134a aus mobilen Klimasystemen, Dr. Winfried Schwarz.
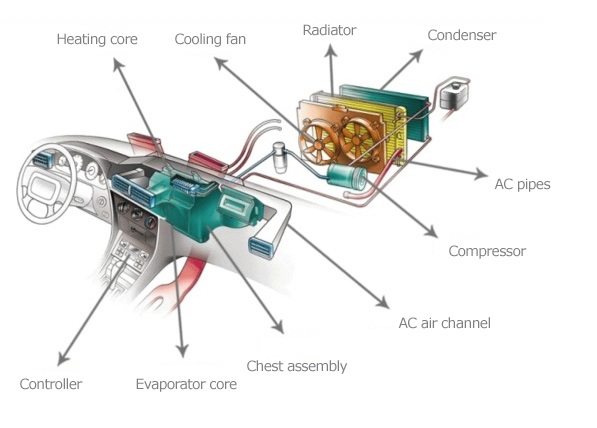
Wie eine Klimaanlage funktioniert
Das Kältemittel wird mit Hilfe des Verdichters unter Druck gesetzt. Wenn der Druck und die Temperatur des Kältemittels steigen, wird es flüssig, während es den Kondensator mit einer Temperatur von ca. 60°C passiert. Wenn sich das Fahrzeug bewegt, wird der Kondensator durch die durchströmende Luft gekühlt, in anderen Fällen geschieht dies durch den Kondensatorlüfter. Das unter Druck stehende flüssige Kältemittel strömt durch das Expansionsventil, dehnt sich aus und verliert an Druck. Im Verdampfer verdampft das flüssige Kältemittel und nimmt Wärme auf. Der Verdampfer und die Umgebung kühlen sich von “-10°C” auf “-18°C” ab. Das vom Fahrer gesteuerte Verdampfergebläse drückt die kühle Luft in das Auto. Der Zyklus wiederholt sich, wenn das Kältemittel wieder flüssig wird.
Stickstoff (N)-Verbrauch in Autoklimaanlagen
Stickstoffgas liefert perfekte Ergebnisse in Klimaanlagen. Stickstoff ist ein trockenes und inertes Gas, das billig und leicht zu beschaffen ist. Ein Druckregler ist erforderlich, um den Druck unter Kontrolle zu halten. Geeignete Geräte finden Sie in Geschäften, die Schweißgeräte verkaufen. Für den Anschluss an das vorhandene Klimaanlagenverteilerrohr benötigen Sie außerdem Umschaltverschraubungen.
Stickstoffgas erleichtert die Suche nach Kältemittellecks.
Bei der Suche nach Lecks unter Druck sollte keine Druckluft verwendet werden, die Feuchtigkeit enthält, die der Klimaanlage schadet.
Stickstoff trocknet die Klimaanlage aus und verkürzt die Dauer des Vakuums.
Die Stickstoffbegasung vor dem Befüllen der Anlage mit Kältemittel ist eine wirksame Methode zur Trocknung und Spülung. Zu diesem Zweck wird ein Ende der Klimaanlage zur Atmosphäre hin offen gelassen. Das andere Ende wird an den Klimaserviceverteiler und den Stickstoffschlauch angeschlossen, und dann wird Druckgas in die Anlage geleitet. Auf diese Weise wird die Feuchtigkeit im System entfernt. Ein weiterer Vorteil der Verwendung von Stickstoff ist die Verkürzung der Vakuumdauer in tiefen Ebenen.